Digital Transformation is a mindset, not just a mere adoption of new technologies. It represents a profound evolution in how businesses operate, connect, and deliver value. Rooted in this transformative thought process, we now stand on the cusp of Industry 5.0. This next industrial phase intertwines human intelligence with technological advancements, emphasizing collaboration, personalization, and sustainability. As we explore the details of Industry 5.0, it is critical to recognize this phase as the next chapter in our ongoing digital transformation journey.
What is Industry 5.0?
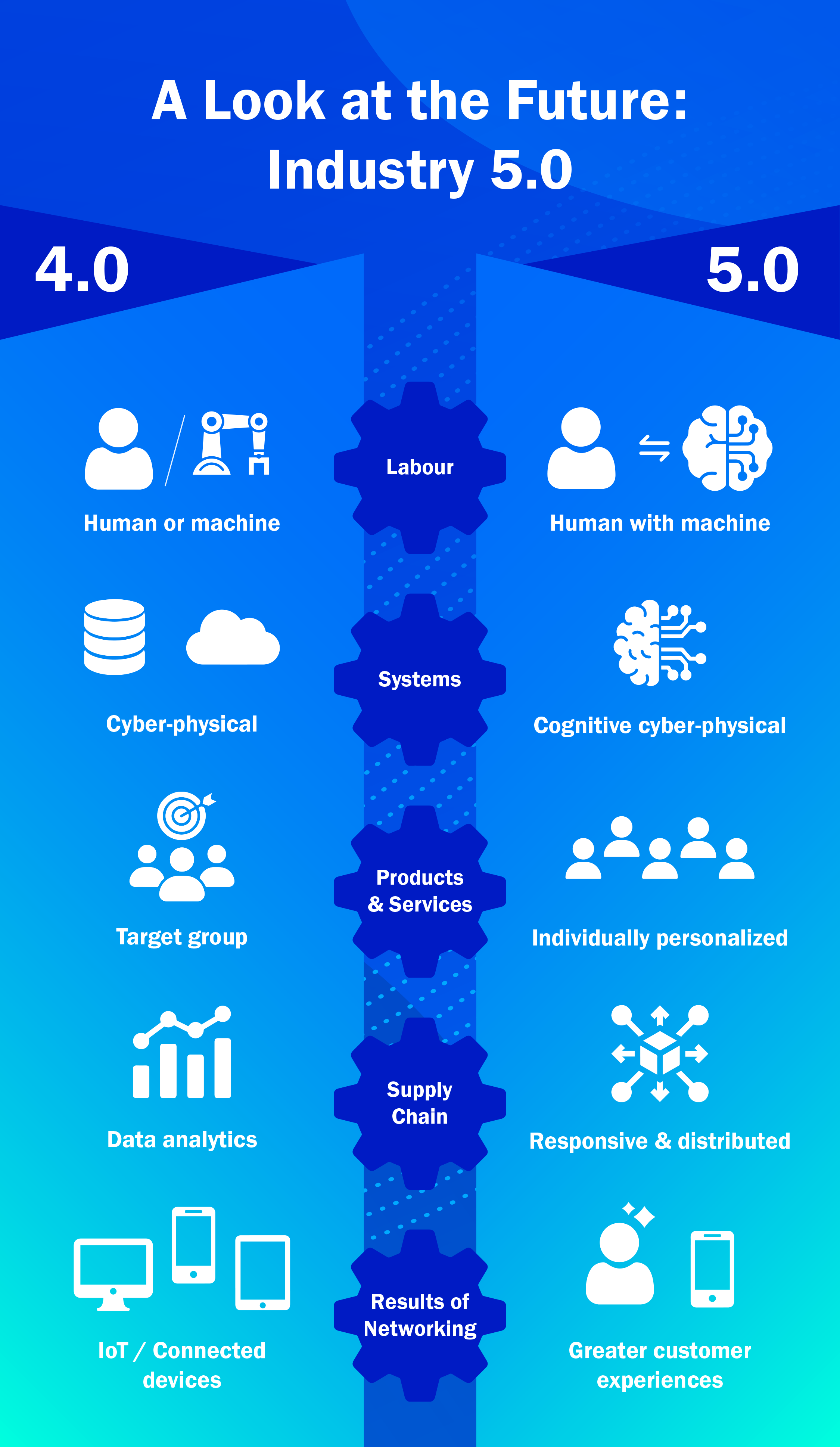
The standards of Industry 4.0 still guide our processes today, but transition to Industry 5.0 has already begun. This phase must not be seen as simply an upgrade over 4.0, but rather, an entirely new paradigm shift. The European Union defines Industry 5.0 as a move beyond the emphasis on efficiency and productivity to anchor industrial undertakings in societal contributions. While integrating cutting-edge technology is important, Industry 5.0 emphasizes the creation of a harmonious partnership between human ingenuity and machine capabilities in manufacturing activities. 5.0 focuses on positioning the human worker at the heart of the processes.
“In our increasingly interconnected world, businesses need to be agile and adaptive, not just to thrive, but to survive. This means ensuring that manufacturing processes are not only efficient but also environmentally sustainable, socially responsible, and economically viable.” -Benny Cohen, KPI Digital
What is the difference between Industry 4.0 and 5.0
Industry 4.0 emerged as a ground-breaking shift, signaling a profound transformation in the manufacturing landscape. This shift was more than an introduction of new tools and systems, it represented an overhaul of how industries perceived and integrated technology. This phase combined 3 major pillars: the Internet of Things (IoT), Information Technology (IT), and Operational Technology (OT). This integration propelled great improvements in manufacturing efficiency and agility, enabling real-time decision-making, enhancing connectivity, and laying down the blueprint for smart factories.
Industry 5.0 however, represents the recentering of humans in the industrial equation. The standards of Industry 5.0 focus on amplifying the human role by ensuring that technology acts as an enabler rather than a replacement. This new generation re-enforces the relationship between man and machine, emphasizing the invaluable human touch, cognitive flexibility, and adaptability. While machines compute and analyze at unparalleled speeds, the irreplaceable human attributes of creativity, empathy, and ethical judgment are paramount for sustainable growth.
Industry 5.0 focuses on 7 major pillars
Human-Machine Collaboration
The idea is not to replace humans but to ensure machines and robots amplify human capabilities. Along a car assembly line, for example, robots perform tasks that require precision or heavy lifting, but a human operator oversees the process, making judgments and performing nuanced tasks. This collaborative robot, or “cobot”, assists the human worker without fully replacing them, ensuring both safety and efficiency.
Production that is More Personalized
With advancements in technology, it is becoming easier to cater to individual customer needs. Industry 5.0 emphasizes tailored manufacturing, allowing for greater product customization while retaining efficiency. Imagine ordering a pair of sneakers online, but instead of choosing from pre-set designs, you customize the shoe’s colors, material, and design elements. This tailored product is then manufactured on-demand and shipped to you, all while maintaining the efficiency of mass production.
Sustainability
Environmental and social responsibility are at the heart of Industry 5.0. It emphasizes cleaner production, waste reduction, efficient energy use, and a commitment to leaving a minimal ecological footprint. If a clothing manufacturer, for instance, decides to transition to a sustainable fashion brand with a reduced carbon footprint, they could choose to use eco-friendly materials, reduce water usage in production, and implement a system to recycle old clothing.
Cognitive Manufacturing
Cognitive Manufacturing involves integrating smart systems and solutions into manufacturing processes. With the aid of AI and machine learning, factories can think, predict, and make decisions based on real-time data. This pillar is key in one’s Digital Transformation journey. The term “cognitive” implies that these systems can learn, adapt, and optimize manufacturing processes in a way that mimics human thought processes.
Decentralization
Industry 5.0 promotes decentralized decision-making, therefore, instead of a central control unit, decisions can be made at various points in the production line, increasing agility and responsiveness. Large beverage companies have factories worldwide. Instead of centrally managing production, each factory is equipped with edge computing capabilities, allowing them to make production adjustments in real-time based on local demand and resources.
Resilience and Flexibility
In an unpredictable world, the ability for industries to quickly adapt and pivot becomes crucial. Industry 5.0 promotes systems and strategies that can quickly respond to changes, whether they are market demands or global disruptions. To respond to a sudden global disruption like Covid, for instance, a tech gadget manufacturer can quickly pivot its supply chain, source its materials locally, and even modify its product lineup to address new market needs, such as producing health-related tech accessories.
Ethical and Social Responsibility
Beyond just profit, Industry 5.0 integrates ethical considerations into business decisions, considering the broader impact on society, workers, and the global community. A toy manufacturer, for example, can choose to avoid any ethical implications of cheap labor, ensure its overseas factories provide fair wages, safe working conditions, and no child labor. They may also invest in local communities, building schools and healthcare facilities as well.
Stay tuned for part 2 of Industry 5.0: A partnership between human ingenuity and machine capabilities, where we explain the digital innovations and applications around Industry 5.0.
Read More: Industry 5.0: Digital Innovations and Applications